Navigating the Ongoing Battle: Understanding the Current Surge of COVID-19 cases in North America, a data-driven analysis.
As 2023 unfolds, the COVID-19 pandemic remains a global health concern, including in North America. The COVID-19 situation in North America is characterized by a dynamic landscape, influenced by a variety of factors including vaccination progress, variants, public behaviour, and seasonal fluctuations. To effectively manage and control the pandemic, countries in North America are employing comprehensive strategies that emphasize public health measures, vaccination, surveillance, and international cooperation. In this article, we will provide an overview of the current COVID-19 status in North America and explore the crucial precautions and preventive measures that are still necessary to contain the virus.
COVID-19 Status in America Region in 2023, Data Snapshot:
Since the onset of the pandemic in 2020 and up to 02 August 2023, a cumulative total of 193,209,590 cases and 2,958,859 deaths were reported in the region of the Americas. From 02-29 July 2023 (EW 27-30), the Region reported 86,451 cases and 1,417 deaths. At the subregional level, COVID-19 cases increased in the Caribbean and Atlantic Ocean Islands, and deaths increased in Central America and the Caribbean and Atlantic Ocean Islands.
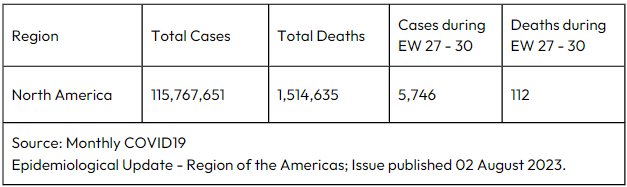
In July 2023, the monthly case notification rate for the region of the Americas was 8.5 cases per 100,000 population. Among 12 countries/territories in the region with available data, COVID-19 hospitalizations increased in 4 countries and territories (range: 7.4% – 100%) during 02-29 July 2023 compared to the previous 4 weeks. Among 11 countries and territories with available data, COVID-19 ICU admissions increased in 2 countries and territories (range: 35.3% – 150%).¹ During this period, the cases and death rate in North America are indicated below table:
Table 1: Cases and deaths in 02-29 July 2023 (EW 27-30) in North America
Factors contributing to the current spike in COVID-19:
- The Variants: One of the most significant factors contributing to the current surge in COVID-19 cases is the prevalence of new variants of the virus. Over the past year, several variants, such as Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Omicron, and Lambda, have emerged, each with unique characteristics and increased transmissibility. These variants have challenged the effectiveness of vaccines and treatment methods, making it harder to control the spread of the virus.
- Vaccination Rates: Vaccination rates have been instrumental in the fight against COVID-19. The availability of vaccines brought hope that the pandemic could be controlled, but vaccine hesitancy and unequal distribution have hindered efforts to reach herd immunity. In some areas of North America, vaccination rates remain low, leaving these communities vulnerable to surges in COVID-19 cases. As of Dec. 7, 2022, over 80% of people in the U.S. had received their first shot to guard against COVID-19 and 68.9% were considered fully vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.²
- Public Fatigue: The ongoing pandemic has taken a toll on people’s mental and emotional well-being. Lockdowns, social distancing, and mask mandates have left many feeling fatigued. As a result, some individuals have become less diligent about following safety guidelines, contributing to the spread of the virus
- Reduced Testing: With the easing of restrictions and a sense of normalcy returning, many people have become less vigilant about testing and monitoring their health. Reduced testing makes it difficult to detect and isolate cases promptly, allowing the virus to spread more rapidly.
- Travel and Gatherings: The resurgence of COVID-19 cases has coincided with increased travel and gatherings. With people returning to domestic and international travel and attending events, the virus has found new avenues for transmission. Crowded places with poor ventilation have become hotspots for outbreaks.
Precautions/Preventive Strategies to Control COVID-19 in 2023:
- Vaccination: Continue to promote, and encourage vaccination for all eligible individuals and facilitate vaccination for eligible individuals, including booster shots for those eligible. Efforts should focus on reaching underserved and hesitant
populations to increase overall coverage.
As of May 11, 2023, a total of 984,444,295 Vaccine Doses were distributed, and 676,728,782 were Administered in the United States according to The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Among them, 2.0M Children under 5 years of age received at least one dose since June 18, 2022. As of May 10, 2023, a total of 81.4% population received the booster dose in the USA.³ - Public Health Measures: Maintain and adapt public health measures based on local transmission rates. These may include mask mandates, social distancing, capacity limits, and indoor ventilation improvements, especially in high-risk settings.
- Testing and Contact Tracing: Sustain accessible and efficient testing and contact tracing infrastructure. Regular testing is crucial for early detection and containment of outbreaks.
- Travel Guidelines: Implement and enforce travel guidelines, including requirements for vaccination or negative COVID-19 tests for travellers. Monitoring and quarantine measures for international travel should be robust.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Continue to educate the public on the importance of adhering to safety measures, getting vaccinated, and staying informed about the evolving situation.
- Indoor Air Quality: Improve indoor ventilation and air quality, as indoor gatherings have been linked to increased transmission during colder months.
- Research and Monitoring: Invest in ongoing research and surveillance to detect new variants and study their impact on vaccine effectiveness. Adapt strategies in real-time based on scientific findings.
- International Collaboration: Cooperate with neighbouring countries on travel restrictions, vaccine distribution, and research. Global collaboration is essential to reduce the spread of the virus.
- Equity in Access: Address disparities in vaccine access and coverage by ensuring equitable distribution and outreach efforts, especially in underserved communities.
¹ https://www.paho.org/en/covid-19-weekly-updates-region-americas
² https://www.usnews.com/news/best-states/articles/these-states-have-the-lowest-covid-19-vaccination-rate
³ https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccinations_vacc-people-booster-percent-pop5